Humidity control is a critical aspect of various industries and applications, ranging from HVAC systems in homes and offices to specialized environments like greenhouses and laboratories. At the heart of these humidity control systems lies the humidity sensor, a device designed to measure and report the amount of moisture in the air. This article delves into the world of humidity sensors, explaining their function, types, working principles, applications, and more.
Understanding humidity control and the role of humidity sensors is crucial for anyone involved in industries where precise environmental control is necessary. Whether you’re a HVAC technician, a greenhouse manager, or a curious homeowner, this comprehensive guide will provide you with a deep understanding of humidity sensors and their importance in maintaining optimal humidity levels.
What is a Humidity Sensor?
A humidity sensor, also known as a hygrometer, is a device that measures the amount of water vapor in the air, soil, or confined spaces. These sensors are integral to systems that control and regulate humidity levels as they provide accurate readings of moisture content in the environment.
The readings from a humidity sensor can be used to maintain the desired humidity level in a specific area. This is particularly important in environments where humidity levels need to be strictly controlled, such as in data centers, greenhouses, or industrial manufacturing facilities.
Types of Humidity Sensors
There are several types of humidity sensors, each with its own unique method of detecting and measuring humidity levels. The most common types include capacitive, resistive, and thermal humidity sensors.
Capacitive humidity sensors measure humidity by observing the change in capacitance of a capacitor. The sensor is designed such that the capacitance changes with fluctuations in humidity levels. Resistive humidity sensors, on the other hand, operate by measuring the change in electrical resistance of a hygroscopic material. The resistance changes as the material absorbs or releases water vapor.
Thermal humidity sensors use heat to measure humidity levels. They consist of two thermal sensors – an exposed sensor and a reference sensor. The exposed sensor is coated with a moisture-absorbing material. As the humidity changes, the material absorbs or releases moisture, causing a change in temperature and, consequently, a change in resistance. The reference sensor remains unaffected by humidity and serves to provide a baseline for comparison.
How Does a Humidity Sensor Work?
The working principle of a humidity sensor depends on its type. However, the basic principle involves the sensor detecting changes in physical or electrical properties as the humidity changes. These changes are then converted into electrical signals which can be measured and interpreted by the system.
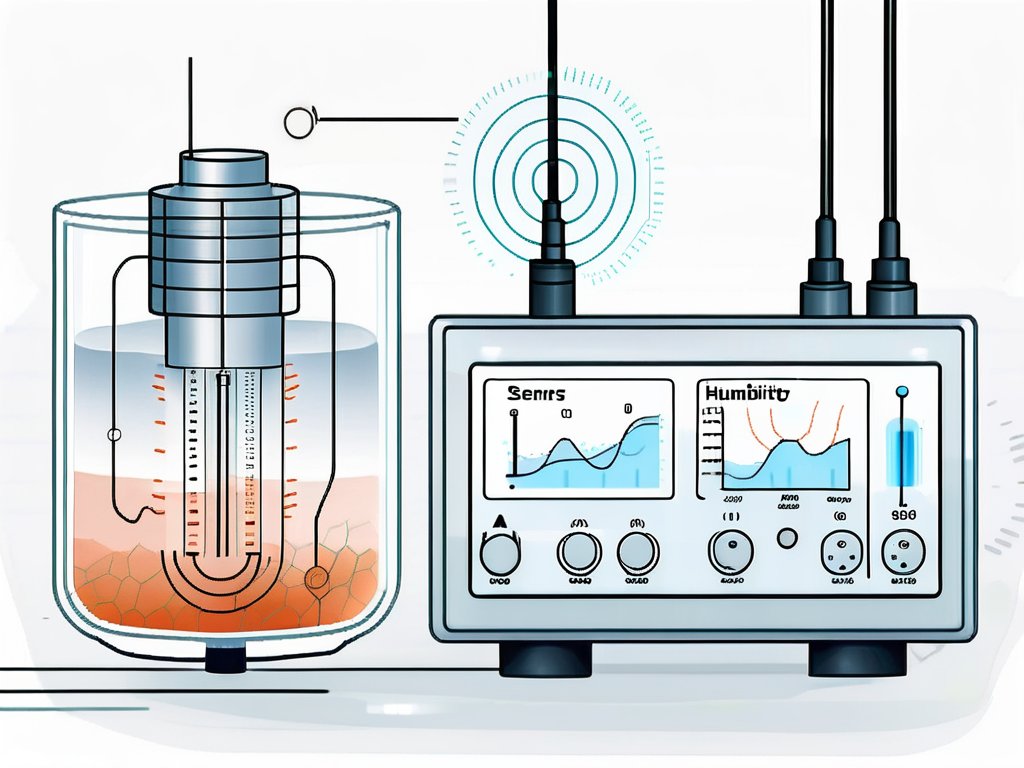
For instance, in a capacitive humidity sensor, the sensor consists of a thin film polymer capacitor. This capacitor has a dielectric that changes its capacitance as it absorbs or releases water vapor. The change in capacitance is then converted into a voltage signal which is proportional to the humidity level.
Interpreting Humidity Sensor Readings
Humidity sensors provide readings in the form of relative humidity (RH). Relative humidity is the ratio of the current absolute humidity to the highest possible absolute humidity (which depends on the current air temperature). A reading of 100% RH indicates that the air is completely saturated with water vapor and cannot hold any more, leading to the possibility of rain. This reading is essential to many processes in various industries.
The readings from humidity sensors can be displayed on a digital screen or used by an automated system to control the humidity level. For instance, in an HVAC system, the humidity sensor’s readings can trigger the system to add or remove moisture to maintain the desired humidity level.
Applications of Humidity Sensors
Humidity sensors are used in a wide range of applications, both in industrial and residential settings. They are crucial in any system that requires precise control of humidity levels.
In the HVAC industry, humidity sensors are used to control the humidity level in buildings and homes. They are also used in greenhouses to maintain the optimal humidity level for plant growth. In the industrial sector, humidity sensors are used in processes that require a specific humidity level, such as the production of pharmaceuticals and food processing.
Humidity Sensors in HVAC Systems
In HVAC systems, humidity sensors play a crucial role in maintaining a comfortable and healthy indoor environment. They provide the necessary data to the HVAC system, allowing it to control the indoor humidity level effectively.
By controlling the humidity level, HVAC systems can prevent problems such as mold growth, which can lead to health issues. Additionally, maintaining the right humidity level can improve indoor comfort by preventing dry skin and throat.
Humidity Sensors in Greenhouses
In greenhouses, maintaining the right humidity level is crucial for the growth and development of plants. Humidity sensors provide the necessary data to the greenhouse’s control system, allowing it to adjust the humidity level as needed.
By controlling the humidity level, greenhouses can prevent problems such as plant diseases and poor plant growth. Additionally, maintaining the right humidity level can improve plant health and yield.
Maintaining and Calibrating Humidity Sensors
Like any other device, humidity sensors need to be maintained and calibrated regularly to ensure their accuracy and reliability. This involves cleaning the sensor, checking its performance, and recalibrating it if necessary.
Calibration involves comparing the sensor’s readings with a known humidity level (usually provided by a reference humidity generator) and adjusting the sensor’s output to match the reference. This process ensures that the sensor’s readings are accurate and reliable.
When to Calibrate Humidity Sensors
The frequency of calibration depends on the sensor’s application and the level of accuracy required. For instance, in critical applications such as pharmaceutical production, sensors may need to be calibrated more frequently.
As a general rule, humidity sensors should be calibrated at least once a year. However, if the sensor is used in a harsh environment or if high accuracy is required, more frequent calibration may be necessary.
Choosing the Right Humidity Sensor
Choosing the right humidity sensor depends on several factors, including the required accuracy, the operating environment, the range of humidity to be measured, and the cost.
For instance, if high accuracy is required, a capacitive humidity sensor may be the best choice. On the other hand, if the sensor will be used in a harsh environment, a thermal or resistive humidity sensor may be more suitable. Additionally, the cost of the sensor may also be a deciding factor.
Considerations When Choosing a Humidity Sensor
When choosing a humidity sensor, it’s important to consider the sensor’s accuracy, response time, range, and stability. The sensor’s accuracy is its ability to provide a correct reading. The response time is the time it takes for the sensor to respond to changes in humidity. The range is the range of humidity levels that the sensor can measure.
The stability of the sensor refers to its ability to maintain its performance over time. A stable sensor will provide reliable and consistent readings, even after prolonged use. Other considerations may include the sensor’s size, cost, and ease of installation.
Conclusion
Humidity sensors play a crucial role in many industries and applications, providing accurate and reliable measurements of humidity levels. Whether you’re controlling the climate in a greenhouse, maintaining comfortable conditions in a home or office, or ensuring the quality of pharmaceutical products, humidity sensors are an essential tool.

With a deep understanding of how these sensors work, their types, applications, and maintenance requirements, you can make informed decisions when implementing or maintaining a humidity control system. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more advanced and efficient humidity sensors in the future.