Have you been searching day and night for a comprehensive list of air pollution sources? Well, look no further! We’ve compiled a helpful master list of all the various air pollution sources, indoors and out, ranging from fireplaces to pesticides.
We created this guide to educate homeowners about the various indoor and outdoor sources of air pollution, how they produce said air pollution and how they affect human health. First, let’s take a look at indoor originating sources. Then, we’ll move on to outdoor pollution sources.
Air Pollution Sources
According to the Environmental Protection Agency, most air pollutants that worsen indoor air quality originate indoors. Meaning indoor sources make up more of the indoor air pollution burden compared to outdoor sources. Nevertheless, outdoor sources still affect indoor spaces. A majority of originating outdoor air pollution exposure occurs indoors.
It’s important to differentiate between indoor and outdoor sources. More often than not, you have greater control over indoor sources. Discovering that certain household products, a lack of HVAC maintenance or storing chemicals like paints and fertilizers are all indoor sources can jumpstart change. With the right information, you can take immediate and individual action against many indoor originating air pollution sources. While with outdoor originating sources, reducing pollution exposure requires change at a greater level such as the community or state.
Regardless, naming indoor and outdoor air pollution sources helps build a better indoor air quality awareness. And choosing any IAQ control intervention strategies or whole-home solutions limits your and your family’s air pollution exposure.
Indoor Air Pollution Sources
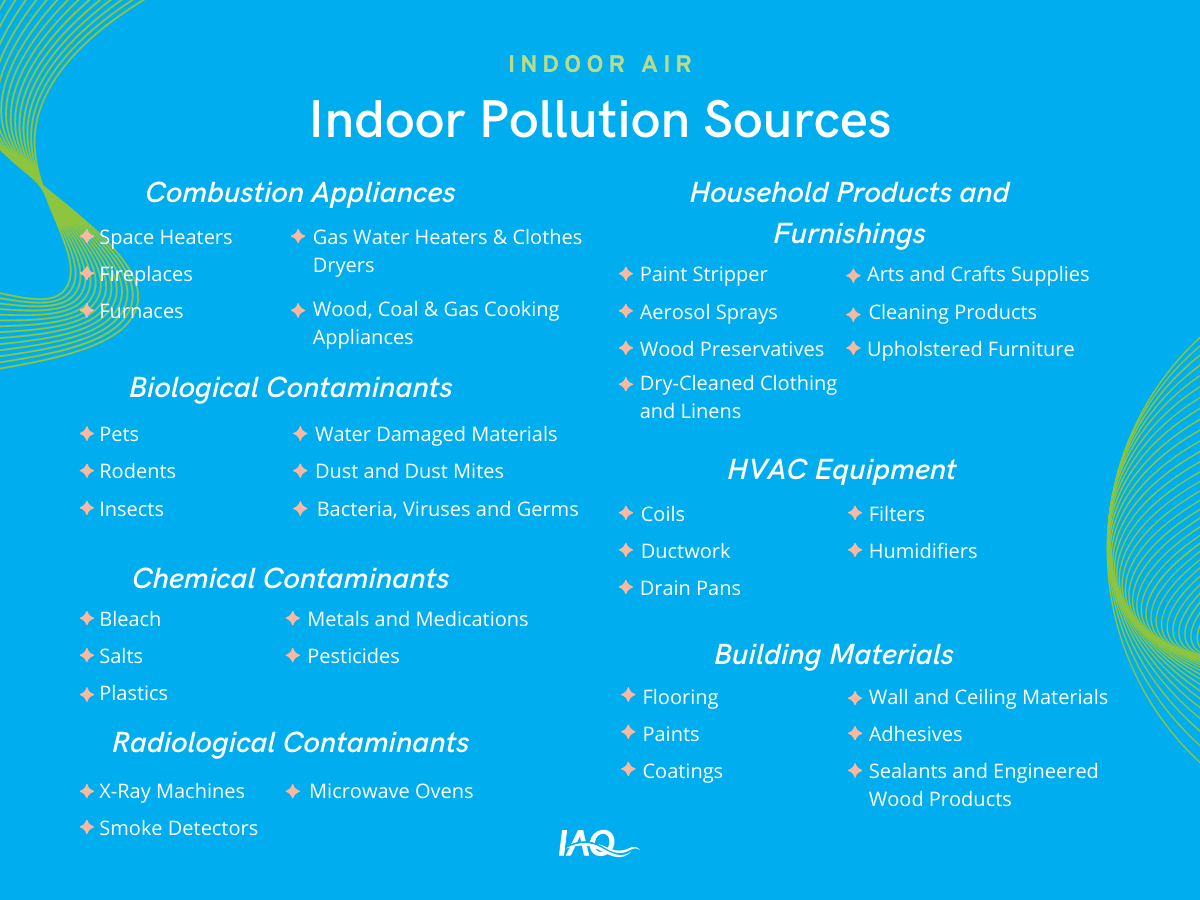
Combustion Appliances
Combustion appliances produce combustion pollutants when burning kerosene, charcoal or tobacco. These combustion-resulting pollutants include carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, particulate matter and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Health effects from combustion pollution exposure include symptoms like headaches, nausea, confusion, respiratory infections, lung cancer and premature death.
Household Products
In reality, household products are a far-reaching category, ranging from disinfectants to hairspray. Household products are found in most homes across America that we rely on for daily use. Some household products are also chemical contaminants and building materials. Many household products emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) such as formaldehyde. Exposure to VOCs may result in short- and long-term effects including headaches, nausea, nosebleeds, liver damage and cancer risks.
Biological, Chemical and Radiological Contaminants
Biological contaminants, also known as microbes or microbiological contaminants, are alive or produced by living beings. This includes bacteria, viruses, mold, mildew, skin and pet dander, saliva, dust mites and droppings. Health effects range from sneezing, watery eyes and coughing, to fever and hypersensitivity pneumonitis.
 Healthy Home IAQ: Creating a healthy home requires indoor air pollution control. IAQ control strategies and products fall into five main categories. Learn which options are available to intervene in your home and how to take action →
Healthy Home IAQ: Creating a healthy home requires indoor air pollution control. IAQ control strategies and products fall into five main categories. Learn which options are available to intervene in your home and how to take action →Chemical contaminants are elements, such as those found on the periodic table. They are also compounds or a mixture of elements. Chemical contaminants can be natural or man-made such as lead, mercury, formaldehyde, methanol and nitroglycerin. Exposure symptoms can include dermatitis, infertility, cancer and heart failure.
Radiological contaminants are unbalanced chemical elements. In other words, they have an uneven number of protons and neutrons. Their unstable atoms emit ionizing radiation, a type of energy from electromagnetic waves or particles. Radioactive elements include radon, strontium-85, uranium-235 and nickel-63. Health effects include but are not limited to acute radiation syndrome, cutaneous radiation injury and cancer.
Building Materials and Furniture
There are two types of building materials found in homes and furniture, type one and type two. Each has its impact on indoor air pollution. Type one materials off-gas contaminants for a short period, while type two materials off-gas contaminants for an extended period.
Additionally, installation sequencing and materials encapsulation impact indoor air pollution when performed improperly. Installation sequencing refers to the order in which new materials are installed. Materials encapsulation refers to the barrier between building materials and indoor air.
HVAC Equipment
When HVAC equipment is poorly designed, improperly installed or not maintained, your home HVAC system poses an IAQ threat. HVAC equipment may harbor biological contaminants which cause health issues such as dizziness, lethargy, shortness of breath and digestive problems.
Examples of Indoor Sources
Outdoor Air Pollution Sources
Outdoor air pollutants enter indoor spaces through infiltration AKA cracks and openings in the building envelope, as well as through the HVAC system and open doors and windows.
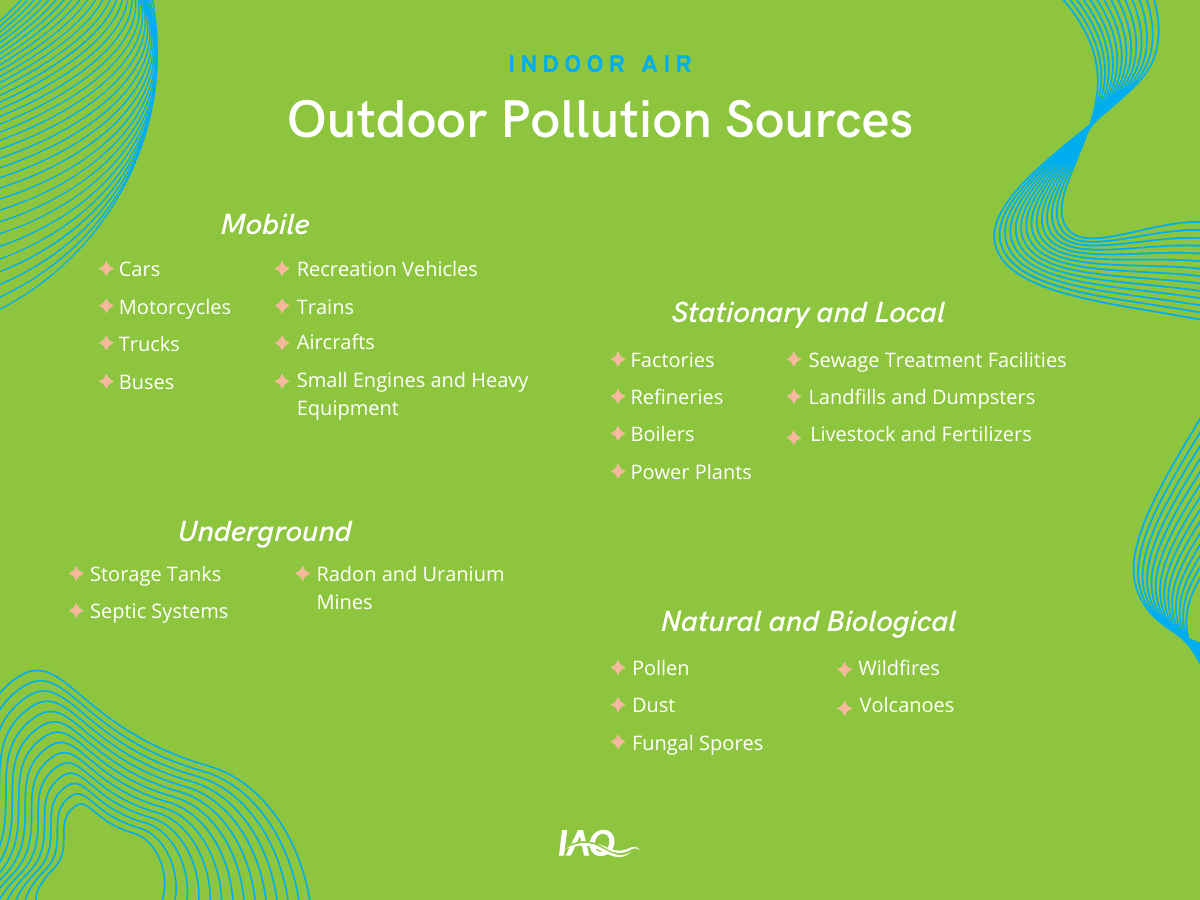
Mobile Source
Mobile sources produce pollution when operating. These pollutants include greenhouse gasses, VOCs, particulate matter and carbon monoxide. Health effects span headaches, fatigue nausea, liver and kidney damage and premature death.
Natural Sources
Natural sources unintentionally produce outdoor air pollution. Contaminants from natural sources include carbon monoxide, particulate matter, sulfur dioxide and nitric oxide. Health effects can include respiratory illnesses, heart failure and premature death.
Stationary and Area Sources
Similar to mobile sources, stationary and local sources produce pollution when operating. This results in particulate matter, carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, mercury and phosphorus pollution among others. Symptoms from stationary source exposure include respiratory illnesses, allergic reactions and premature death.
 Outdoor Air Pollutants: Outdoor sources, especially stationary and local sources, mean that where you live matters. Your location, climate, state or community’s regulations, proximity to outdoor sources and even neighbor’s habits all affect your space’s indoor air quality. Here’s how power plants hurts neighboring communities →
Outdoor Air Pollutants: Outdoor sources, especially stationary and local sources, mean that where you live matters. Your location, climate, state or community’s regulations, proximity to outdoor sources and even neighbor’s habits all affect your space’s indoor air quality. Here’s how power plants hurts neighboring communities →Underground Sources
Yes, there are even sources of pollution underground that affect us aboveground! Underground pollutants are radioactive contaminants, methane, carbon dioxide, radon and phosphorus. Health effects from exposure include risks like respiratory illnesses and cancer.
Examples of Outdoor Sources
Air Pollution Sources Are Everywhere
It’s extremely important to know the many different air pollution sources. However, it can be difficult to remember all of those sources. That’s why we created this master list for homeowners like you to return to again and again as you work to better understand how air pollution sources affect your space. Consequently, be sure that you are doing all that you can do to protect yourself and your family from indoor and outdoor air pollution.