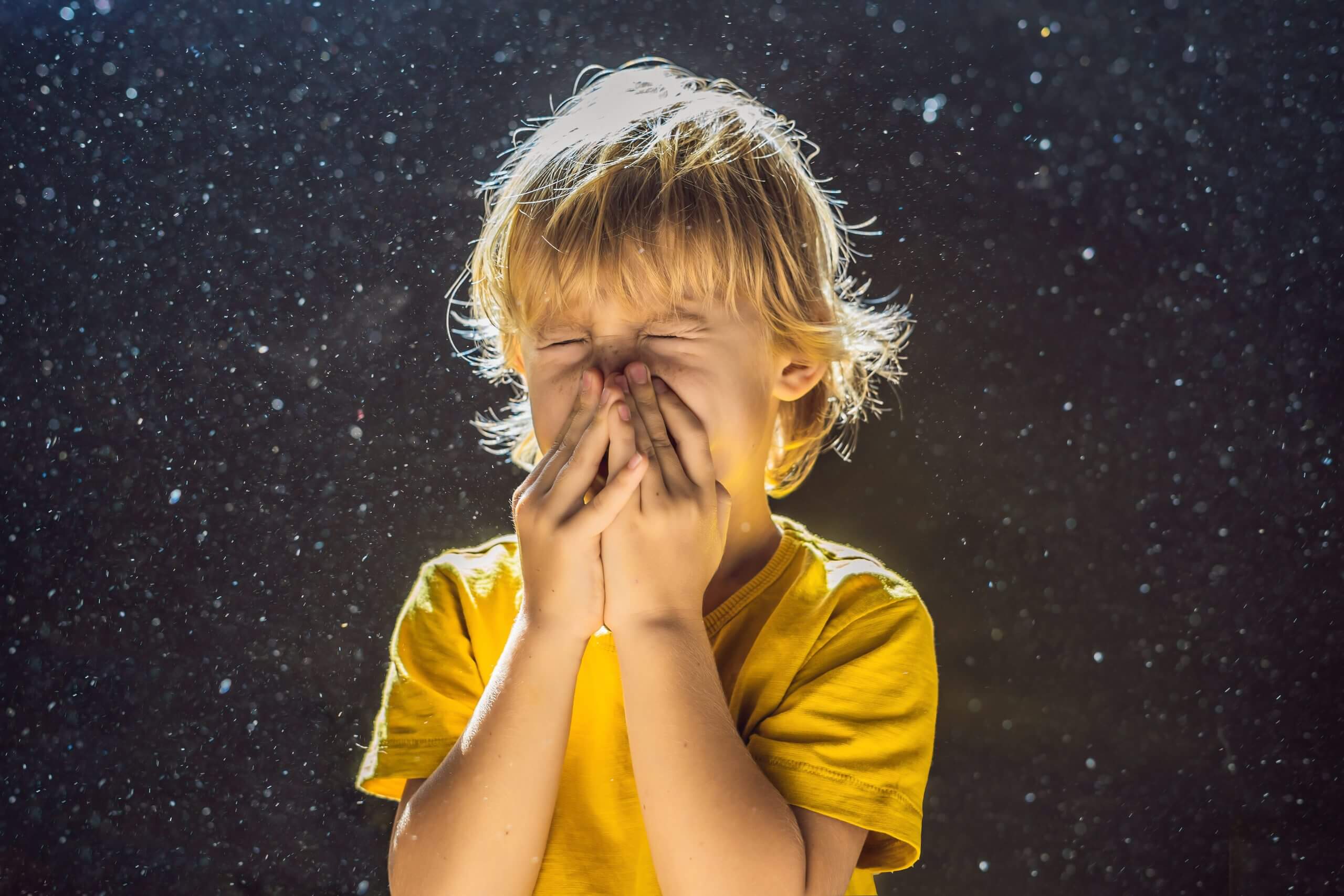
Every single home and indoor space has indoor air pollutants. And the potential health risks of indoor air pollution exposure impacts everyone. There are many sources of indoor air pollution–some of which are unavoidable and some that seem inescapable. Nevertheless, it’s important to understand the potential sources, types of indoor air pollutants and common pollutants likely affecting your home. Indoor air quality control solutions as well as healthy home habits can help improve air quality and reduce the number of indoor air pollutants!
What Are Indoor Air Pollutants?
Air pollution is the release of harmful materials into the environment. Indoor air pollution is simply the release and build-up of harmful materials indoors, or contamination of indoor air. Pollutants can originate from chemical, biological or physical sources. These sources can come from within the home and from outside. Factors like location, environment and outdoor air quality as well as the products used indoors and number of occupants all impact indoor air quality and pollution. Indoor air pollutants can also be found throughout the home–from the living room to the kitchen to the garage and everywhere in between.
Types of Pollutants
There are many different types of indoor air pollutants and potential sources of indoor pollution. Some of the more common pollutants that are likely to affect your living and working spaces can be (roughly) narrowed down to three categories. They are: biological pollutants, chemical pollutants and hazardous air pollutants. Common indoor air pollutants and sources of air pollution differ across the globe. In America, there are a number of major, more frequently found, indoor air pollutants to be aware of.
Biological Pollutants
Like the name, biological pollutants stem from biological sources. You can also think of them as live pollutants, or from living sources. This category includes: germs, viruses, molds, animals and human sources. Biological pollutants can also be airborne. This type of indoor air pollutant is a common trigger for asthma and allergy sufferers as pollutants like cockroaches, dust mites and animal dander can all worsen respiratory symptoms.
Common Biological Pollutants
- Bacteria, Germs and Viruses
- Mold
- Animal Dander
- Dust Mites
- Cockroaches
- Pollen
Chemical Pollutants
Chemical pollutants are usually caused by man-made materials and activities. These pollutants also includes organic chemical pollutants which are formed either by living organisms or man-made chemicals based on natural elements. Modern living has made us largely reliant on chemicals despite the fact that they pollute air, water and food. In fact, many regular household products and materials use chemicals as ingredients, emitting volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in your home. VOCs are emitted from man-made chemicals. There are a plethora of VOCs, but one of the most commonly known is formaldehyde.
Common Chemical Pollutants
- Carbon Monoxide
- Ozone
- Tobacco Smoke / Secondhand Smoke
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
- Radon
- Pesticides
Hazardous Air Pollutants
Hazardous air pollutants are also referred to as toxic air pollutants or simply air toxics. Toxic air pollutants are particles that are toxic or harmful to human life and/or the environment. The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) defines air toxics as pollutants either known or suspected to cause cancer, birth defects or other serious health and environment effects. The EPA currently regulates 187 hazardous air pollutants. This category of pollutants includes gas, aerosol and particulate pollutants–all of which are toxic even in low concentrations and widespread. Hazardous air pollutants are caused by a number of sources such as vehicle emissions, industrial emissions, fuel combustion processes and some building materials.
Common Air Toxics
- Asbestos
- Lead
- Arsenic
How Does Indoor Air Pollution Affect You?
The main way that indoor air pollution affects you: health. However, indoor air pollutants won’t affect everyone in the space the same way. There is a wide spectrum of potential health risks from air pollution exposure. Less serious health symptoms range from throat, ear and eye irritation to shortness of breath, coughing and wheezing. More consequential health affects include higher risks of COPD, pneumonia and cancer. Serious health risks and diseases are also more likely with long-term exposure. And for those that already suffer from asthma, allergies or respiratory conditions, indoor air pollutants can worsen symptoms.
It’s important to note that air pollution exposure indoors can actually be worse than outdoors. The common assumption that outdoor air quality has greater health consequences is a misconception. According to the CDC, indoor air pollution exposure is worse because we spend more time indoors and most indoor spaces suffer from high pollution levels. That is, spaces without IAQ solutions or healthy home habits!
Reducing Indoor Air Pollutants
To effectively reduce the number of indoor air pollutants in your space, we suggest taking measures to better control the air indoors. Thankfully, there is more than one way to improve your indoor air quality. And choosing the best indoor air quality control solution doesn’t even have to be a single choice. Rather, you can pursue a combination of control options from the main five IAQ control strategies: source control, humidity control, filtration, purification and ventilation. All of which help reduce indoor air pollutants in your home.
Source control is a combination of efforts, but primarily, it’s simply having a greater awareness of the sources and habits that impact indoor air quality. With increased awareness, simple fixes include choosing eco-friendly, less toxic cleaning products or vacuuming and changing bedding more frequently.
The health benefits of humidity control should not be overlooked. Proper indoor humidity regulation is a wildly beneficial method to reduce indoor air pollutants, specifically homes suffering from dust mites or mold. The survival of both biological pollutants depends on high moisture levels. Meaning, a whole-home dehumidifier to keep humidity levels in the ideal 40-60% range would help.
Improving ventilation means more fresh air and better air quality overall. Also, good ventilation helps minimize exposure to chemical pollutants like VOCs. The best way to upgrade home ventilation is through a whole-home mechanical ventilation system. Or at least, utilize localized spot ventilation when cooking, showering or using household cleaning products.
Creating Good IAQ
In the end, the most helpful control method is the one that works best for you and your space. Whatever way you choose to intervene in your home’s air quality, it will provide beneficial results and noticeable improvements.