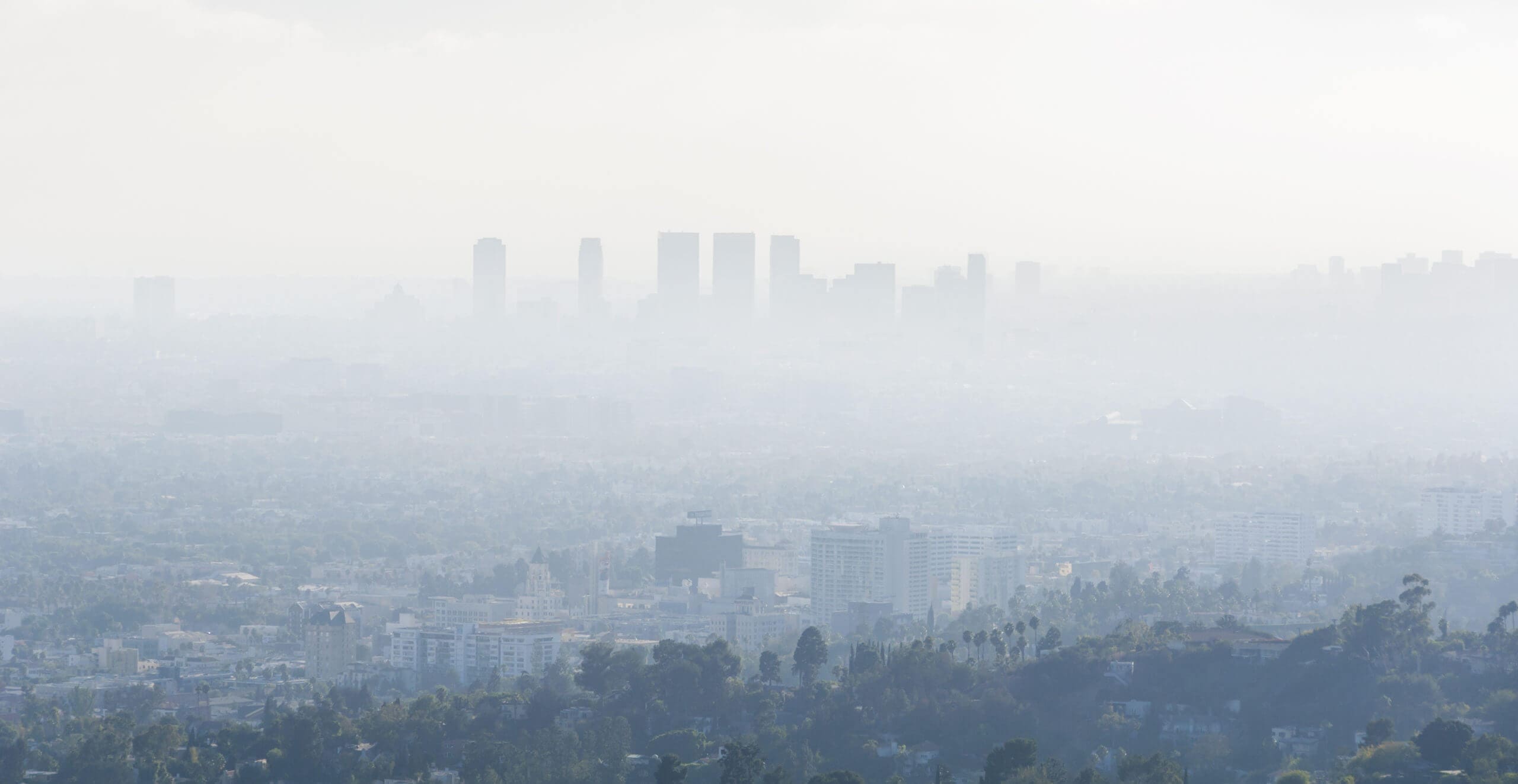
The 2020 State of the Air report from the American Lung Association revealed that 45.8% of the U.S. population lives in areas with polluted outdoor air. The data is measured by county and accounts for roughly 150 million people. That means almost half of America is breathing in polluted air with unsafe levels of either ozone or particulate pollution, two common outdoor air pollutants. That’s a significant amount of the population.
Unfortunately, polluted air is an issue that is not limited to the outdoors. Air pollution is both inside and outside, and sadly, often worse indoors. This is partly because there are both indoor and outdoor sources of pollutants that affect the quality of indoor spaces. Pollutants can enter homes and buildings and affect the air quality.
So, what exactly are these outdoor air pollutants that contaminate indoor air? Where do they come from, and how do they further reduce the quality of indoor air?
Common Sources of Outdoor Air Pollutants
What are common outdoor air pollutants and where do they come from? They can originate from both natural and human-caused sources. There are a couple main categories of outdoor pollutants. The first are criteria pollutants which are known to cause health and environmental problems. The six criteria pollutants are: carbon monoxide, lead, nitrogen dioxide, ozone, particulate matter and sulfur dioxide. All are quite common outdoor air pollutants. The second category is air toxics. These are defined as hazardous pollutants because they are known to cause serious health problems like cancer and reproductive issues. The EPA’s list comprises 650 chemicals that are toxic pollutants.
One’s exposure to outdoor air pollutants is dependent on lifestyle and location. These factors impact to what degree outdoor pollutants are worsening your home’s indoor air or the health of your space. Learning where these pollutants come from is one of the keys for indoor pollution source control.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors will be largely dependent on one’s region and even specific location. The amount, type and levels of outdoor air pollutants in your area are dependent on factors like how close your home is to specific locales such as landfills and the amount of pollen in the air during a specific season.
It is quite easy to unintentionally bring in outdoor materials like soil, dusts and allergens when entering homes and buildings. They stick to surfaces like clothes, shoes and bags. However, what exactly one is bringing in will depend on current environment factors.Waste facilities, like dumpsters and landfills, are also sources of pollutants. They not only pollute the air, they also contaminate soil and nearby water sources. This is a huge concern, seeing as America generates roughly a quarter of a billion tons of garbage each year.
Mobile Sources
Cars, trucks and equipment engines are all considered mobile sources of air pollution. Equipment or non-road engine emissions are machines that also use internal combustion engines. This could include heavy machinery used in construction, as well as things like generators or lawn-care machinery. Together, these sources account for over half of all air pollution in the United States.
Mobile sources generate harmful pollutants like ozone, particulate matter, carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons. They also increase levels of sulfur dioxides and a wide array of greenhouse gases in outdoor air.
Industrial Emissions
Industrial emissions come from stationary sources, such as power plants, factories and industrial facilities. For facilities like these, many activities rely on the use of combustion. Their processes also create dust, heavy metal particles and harmful gases. All of this contributes to outdoor air pollution.
Industrial emissions are similar to those produced by mobile sources. They also contribute to particle pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. Industrial sites often produce waste matter that can also cause air pollution.
How Outdoor Air Enters Homes and Buildings
Outdoor air can enter homes, commercial buildings and all indoor spaces through natural ventilation. This happens through open doors or open windows.
Outdoor air also becomes indoor air through processes of mechanical ventilation. Mechanical ventilation has many benefits for the quality of your home’s indoor air. There are different types of ventilation systems that ensure your home has a consistent flow of fresh air. This process means air from outside enters your home through the HVAC system’s outdoor air intake. This can seem like a bit of a catch-22 for limiting pollutants, but, mechanical ventilation has many indoor air quality benefits.Instead, to make sure that it doesn’t increase the level of pollutants in your home, choose a filtered mechanical ventilation system. Another option would be to pair it with upgraded air filters as well, such as the ideal MERV 13.
Infiltration is another way outdoor air enters buildings, and it’s more difficult to control. This occurs when outdoor air seeps into openings in the structure of a building, such as structure cracks or gaps in windows, doors and walls. Studies have shown that it’s likely that 90% of homes in the United States have normalized air leakage. Prioritizing good indoor air quality control methods can combat this.
How Outdoor Air Pollution Impacts Indoor Air Quality
Polluted outdoor air increases the number of indoor air pollutants. This, in turn, results in poorer indoor air quality. Indoor spaces already have a plethora of pollutants caused by indoor sources and factors, so outdoor air pollution simply compounds the issue.
Many studies have shown that poor indoor air quality has a negative health impact on occupants. For starters, researchers associate poor indoor air quality with sick building syndrome (SBS). Studies show that SBS affects between 10 to 25% of all buildings in the U.S. SBS symptoms include headaches and irritated eyes, nose, and throat, as well as dry coughs and dry skin.
High counts of outdoor pollen can also lead to poor indoor air quality. This is usually particularly true for the spring and fall, or when the seasons begin to change and there are shifts in weather and air quality. For instance, the fall season can greatly affect IAQ by increasing allergens and pollens like ragweed. High indoor pollen counts, in turn, can trigger allergies or asthma. They can also cause breathing issues in otherwise healthy people. These are just the start of a number of possible health effects the indoor air quality impacts.
Solutions for Improving Indoor Air Quality
Overall, your indoor air is already more highly polluted than outdoor air. Luckily, there are solutions available to improve indoor air.
The first thing you may want to do is invest in a whole-home high-performance air purifier. The best air purification systems can capture and purify all kinds of contaminants. Whether it’s pollen, bacteria, fungi or dust, air purification systems effectively eliminate them all.
Another option is to replace standard home air filters with high-efficiency air filters. We recommend MERV 13 air filters for every home. It is the ideal upgrade and installation to trap harmful pollutants. If you want to learn more about your home or space’s indoor air quality, IAQ equipment is available that allows one to track air quality. An indoor air quality monitor can be a beneficial tool to have on hand.
Working in combination, indoor air quality upgrades are consistently working to remove harmful air pollutants and particles from indoor air and leave you with a cleaner, healthier system. Indoor air quality control drastically improves poor air quality caused by all pollutants, whether they originate indoors or outdoors.
Choose Clean and Safe Indoor Air
So long as there’s outdoor air pollution, it will continue to affect indoor air quality. This doesn’t mean that your home or building’s indoor air quality should suffer. With the right strategies and solutions, you can make the air inside your home or office healthier and safe once again.