As the homeowner’s advocate, we at IAQ Works think it’s important to explain concepts and terms that frequently arise in HVAC-related discussions. Humidity control is one of the five core IAQ control strategies. The others are purification, ventilation, filtration and source control. A humidity glossary is helpful to create and maintain a comfortable indoor environment. Before we discuss the humidity control terms you need to know, here’s a quick breakdown of humidity and humidity control.
What Is Humidity and Humidity Control?
Homeowners talk about humidity all the time, but what is it actually? Humidity is less complicated than you think. It’s simply a measurement of the amount of water vapor in the air. When there is a significant amount of water vapor present, humidity is high. When there is an insignificant amount of water vapor present, humidity is low.
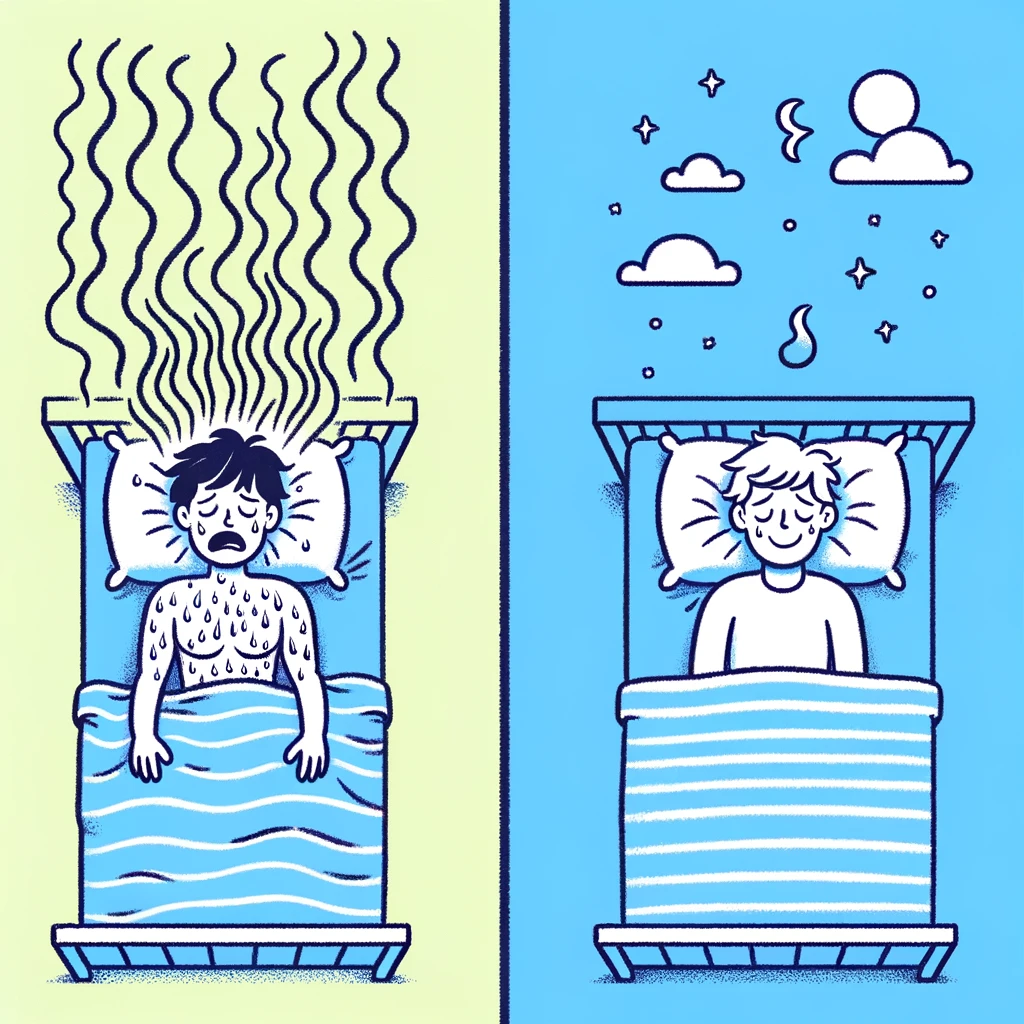
Humidity control is exactly what it sounds like, controlling the humidity in your home. This is done by adding water vapor to the air or removing it, also known as humidification or dehumidification, respectively. Whole-home humidifiers and dehumidifiers work to maintain the ideal 40–60% indoor humidity range. According to research, this range provides numerous health benefits, allowing homeowners to live comfortably.
 Humidity Control: If you’re looking to learn more about humidity control and its benefits as well as the dangers of low and high humidity, check out this guide →
Humidity Control: If you’re looking to learn more about humidity control and its benefits as well as the dangers of low and high humidity, check out this guide →Humidity Glossary
1. Absolute Humidity
Absolute humidity is a measurement of water vapor in the air, regardless of temperature. It is expressed as grams of water vapor per cubic meter of air. As the water vapor concentration increases, so does absolute humidity.
2. Specific Humidity
Specific humidity refers to the mass (amount) of water vapor per unit mass (amount) of air. This is usually expressed as grams of water vapor per kilogram of air.
3. Dew Point
The dew point is the temperature the air must cool to in order to reach 100% relative humidity.
4. Heat Index
The heat index is a measurement of temperature and relative humidity. When the temperature and/or relative humidity are high, the heat index increases. In sum, the heat index allows us to determine how hot it actually feels outside.
5. Water Vapor
Water vapor, also known as moisture, is simply water in its gaseous state. As aforementioned, the amount of water vapor in the air determines humidity.
6. Condensation
Condensation is the opposite of evaporation. This process occurs when water changes from a gaseous state to a liquid. When the air reaches its dew point or it becomes saturated and condensation forms.
7. Evaporation
Evaporation is the opposite of condensation. This process occurs when water changes from a liquid to a gas. When water is heated, its molecules move faster and faster until they become water vapor.
8. Mixing Ratio
The mixing ratio refers to the mass (amount of matter) of water vapor as it compares to the mass of other gases.
9. Saturation
When the air is filled with water vapor, as much as it can possibly hold, it is saturated.
10. Humidistat
A humidistat is similar to a thermostat, except it measures humidity, not temperature. Whole-home humidifiers and dehumidifiers have humidistats. They control the amount of water vapor in the air in order to provide a comfortable living space.
11. Relative Humidity
Relative humidity is a measurement of water vapor in the air, with regard to temperature. Warm air holds more water vapor than cold air. Thus, relative humidity is higher when the air is cold and lower when the air is warm.
A Lesson in Humidity Control
Whether you’re a new homeowner or a seasoned homeowner, HVAC and IAQ terminology can be complicated. That’s why IAQ.Works is here to walk you through every (relevant) term in the dictionary. We advocate for homeowners, so it only makes sense that we educate as well. Gone are the days of foreign conversations with your HVAC technician. Study these humidity control-related terms and move forward with confidence!